“Sepsis: more than 26 million people affected, 9 million deaths per year, 60% of mortality when degenerates in septic shock. The dysregulated inflammatory response is remodulated by extracorporeal adsorption of inflammatory mediators.”
Sepsis is defined as organ dysfunction caused by an irregular response of the host to the infection.
Understanding the general framework of sepsis-guiding mechanisms remains an open challenge and several theories have been proposed with regard to its action.
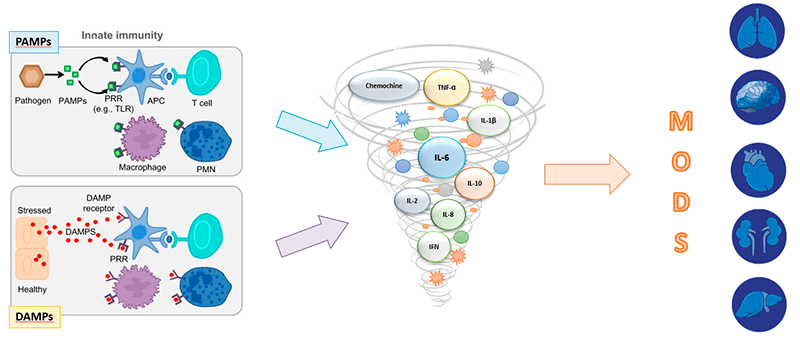
Pathogen-Associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damaged-Associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) have been identified as triggers of the activation of pro-and anti-inflammatory responses.
In fact, the insult, which can be the invasion of the organism by an external microorganism, results in the release of mediators pro and anti inflammatory. When such release is excessive, uncontrolled and spread beyond the site of the outbreak, sepsis develops.
It is a time-dependent syndrome, in which the clinical outcome is strongly dependent on a sudden diagnosis and effective clinical management of the patient.
Septic shock is an evolution of sepsis, in which important circulatory, metabolic and cellular alterations occur, resulting in a substantial increase in mortality.
In septic shock, there is a critical reduction in tissue perfusion which, in turn, can result in multi-organ failure (MOF). In the hypoperfuse areas, during the shock, events of the inflammatory and coagulative cascade occur. In fact, the hypoxic cells of the vascular endothelium activate the white blood cells which in turn bind to the endothelium and release harmful substances. Patients with septic shock can be detected by the combination of sepsis-related clinical picture with persistent hypotension requiring vasopressor.
Multiple extracorporeal therapies have been studied as adjuvant therapy in sepsis, in particular directed to the modulation of the cytokine cascade from the blood, with the aim of favoring the exit from the septic shock, improving the general clinical picture of the patient.
