“New frontiers in the critical patient”
The critical patient is characterized by complex multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), of various aetiology.
The use of apheresis for the purification of blood, in this context, is becoming increasingly important, due to the pathophysiological aspects that are at the base.
The goal is to restore homeostatic disorders and control the numerous toxic molecules released following complex biological reactions.
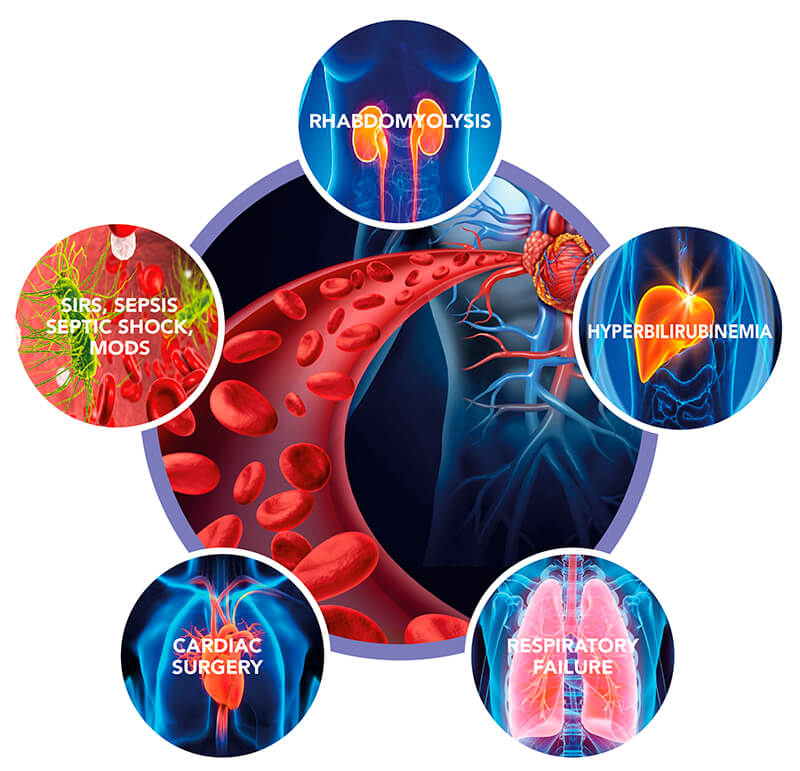
The clinical manifestations of the critical patient are extremely varied, they can present in fact serious infections and sepsis, serious cardiac and respiratory failure, acute renal failure and liver failure.
The application of apheresis is increasingly present also in cardiac surgery, in particular in the cardiac surgery with extracorporeal circulation, in which patients often develop MODS, infections and sepsis in the postoperative period.
